On OpenShift#
The Hibernation Operator is a Red Hat Certified Operator available on the Red Hat Marketplace and OperatorHub in OpenShift.
This document contains instructions for installing, configuring, and uninstalling the Hibernation Operator on OpenShift.
Requirements#
- An OpenShift cluster (v4.10 or higher recommended)
Installing via OperatorHub UI#
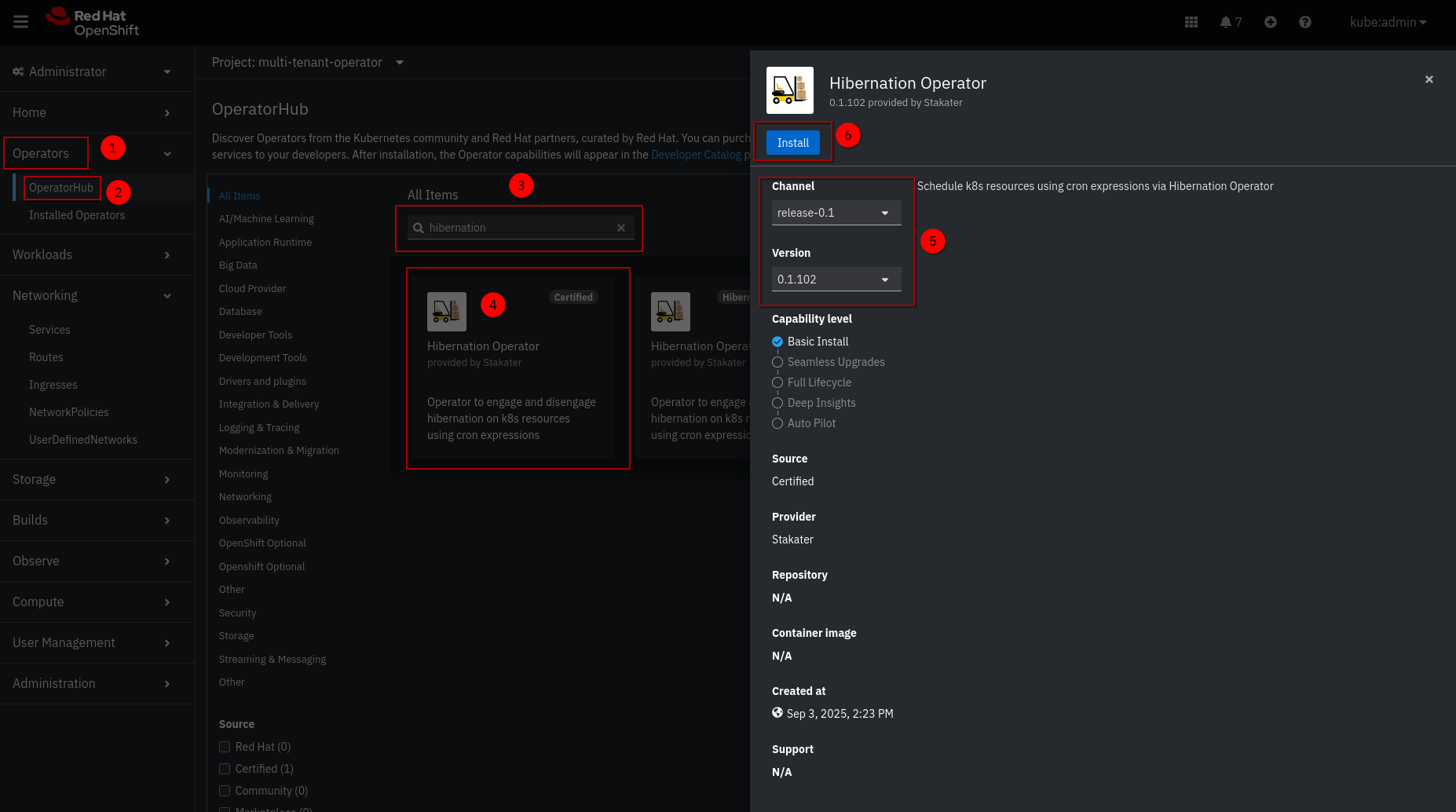
- In the OpenShift Console, navigate to Operators → OperatorHub from the left sidebar.
- Search for
Hibernation Operatorand click on the tile. - Click the Install button.
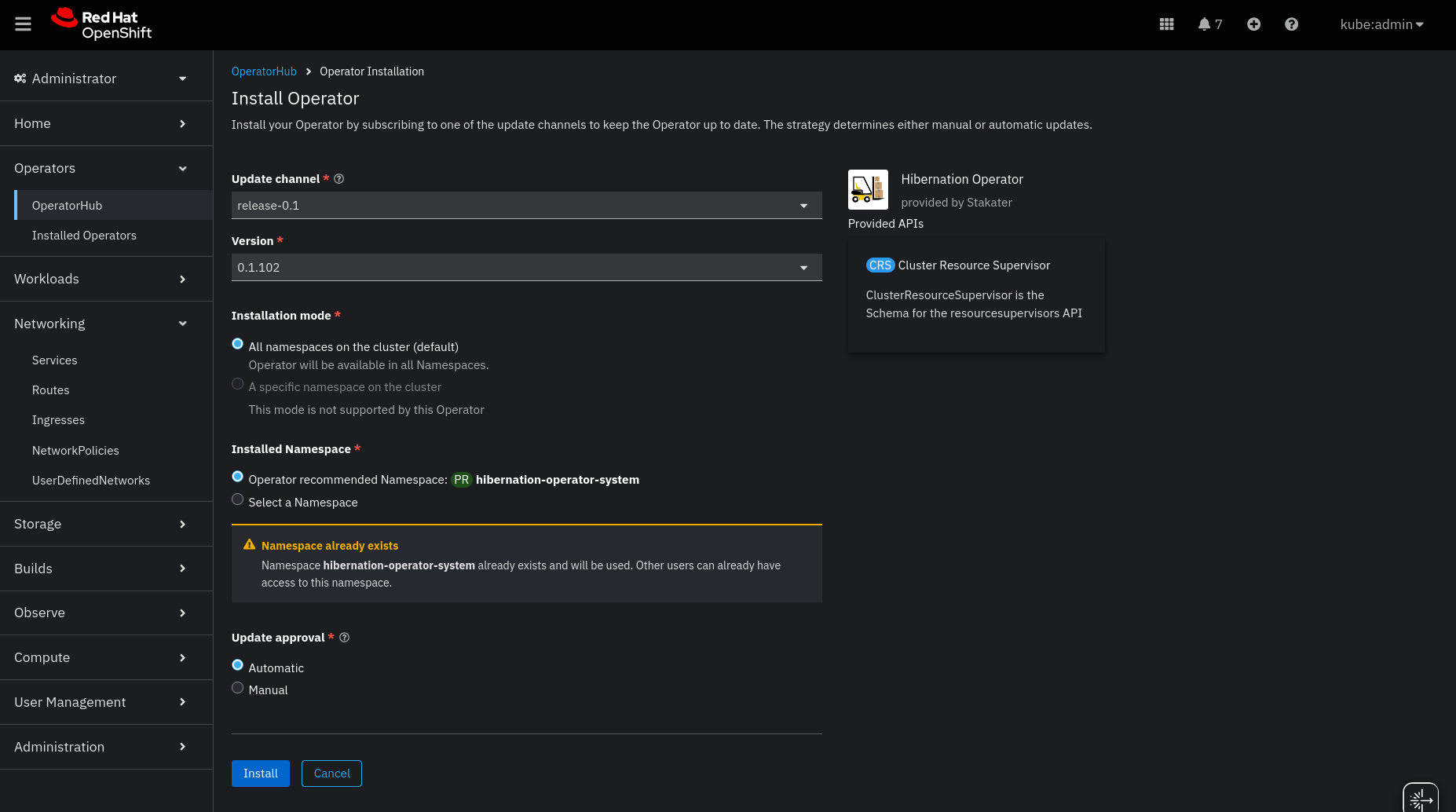
- Configure the installation:
- Update channel:
stable(recommended for production) - Installed Namespace: Select
hibernation-operator-system(create if it doesn’t exist) - Update approval:
Automaticfor developmentManualfor production (allows review of upgrades)
Click Install.
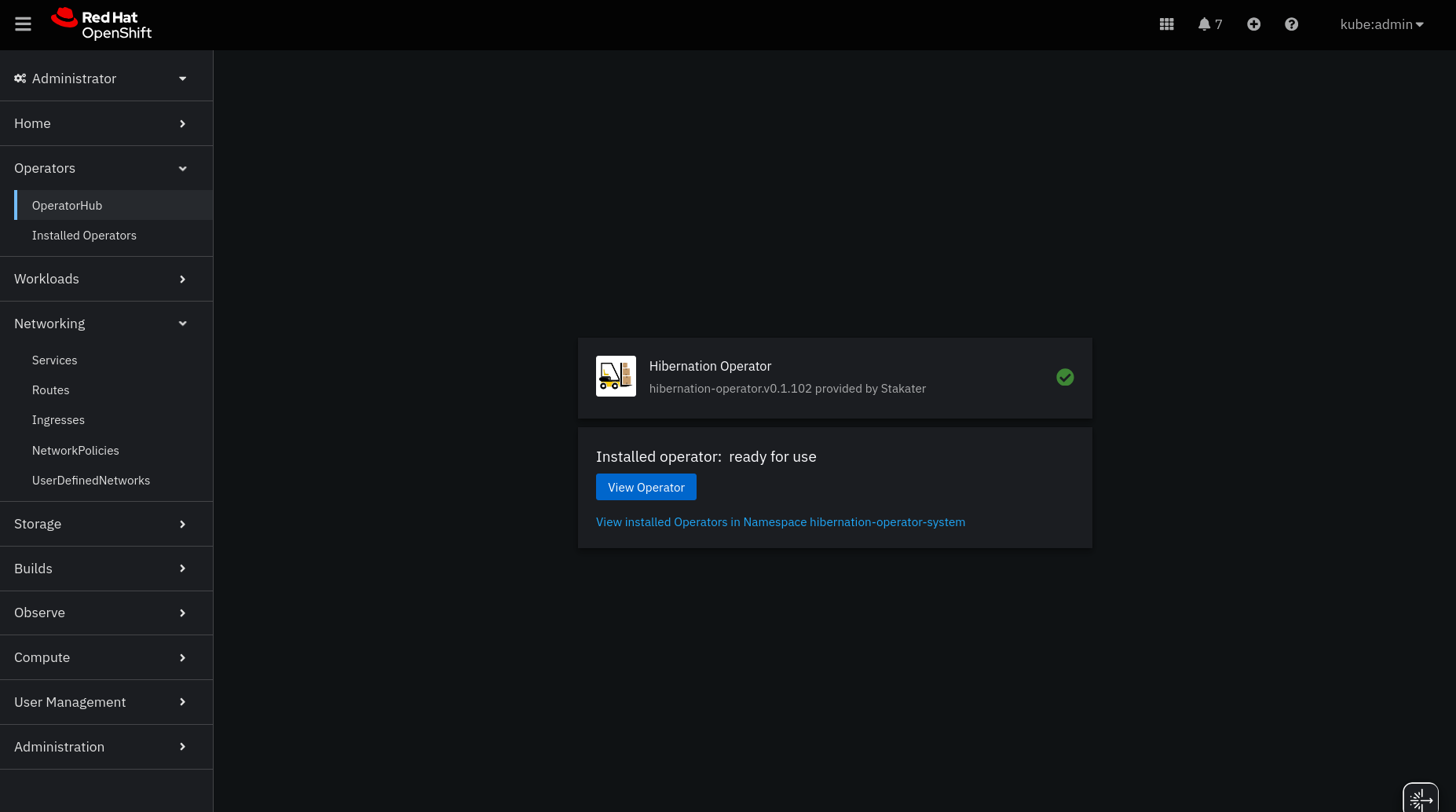
- Wait for the operator to install. You’ll see a status of Installed operator: Ready for use when ready.
- Once installed, the Hibernation Operator is ready to manage hibernation policies across your cluster.
💡 Note: The operator is installed in the
hibernation-operator-systemnamespace by default.
Installing via CLI or GitOps#
Use this method for automation, CI/CD pipelines, or GitOps workflows (e.g., with ArgoCD).
Step 1: Create the Operator Namespace#
oc create namespace hibernation-operator-system
Step 2: Create an OperatorGroup#
oc create -f - << EOF
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1
kind: OperatorGroup
metadata:
name: hibernation-operator
namespace: hibernation-operator-system
spec:
targetNamespaces:
- hibernation-operator-system
EOF
Step 3: Create a Subscription#
oc create -f - << EOF
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: hibernation-operator
namespace: hibernation-system
spec:
channel: release-0.1
installPlanApproval: Automatic
name: hibernation-operator
source: certified-operators
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
# Optional: pin to a specific version
# startingCSV: hibernation-operator.v0.1.102
EOF
✅ GitOps Tip: Commit these YAMLs to your GitOps repo to manage the operator declaratively.
Step 4: Verify Installation#
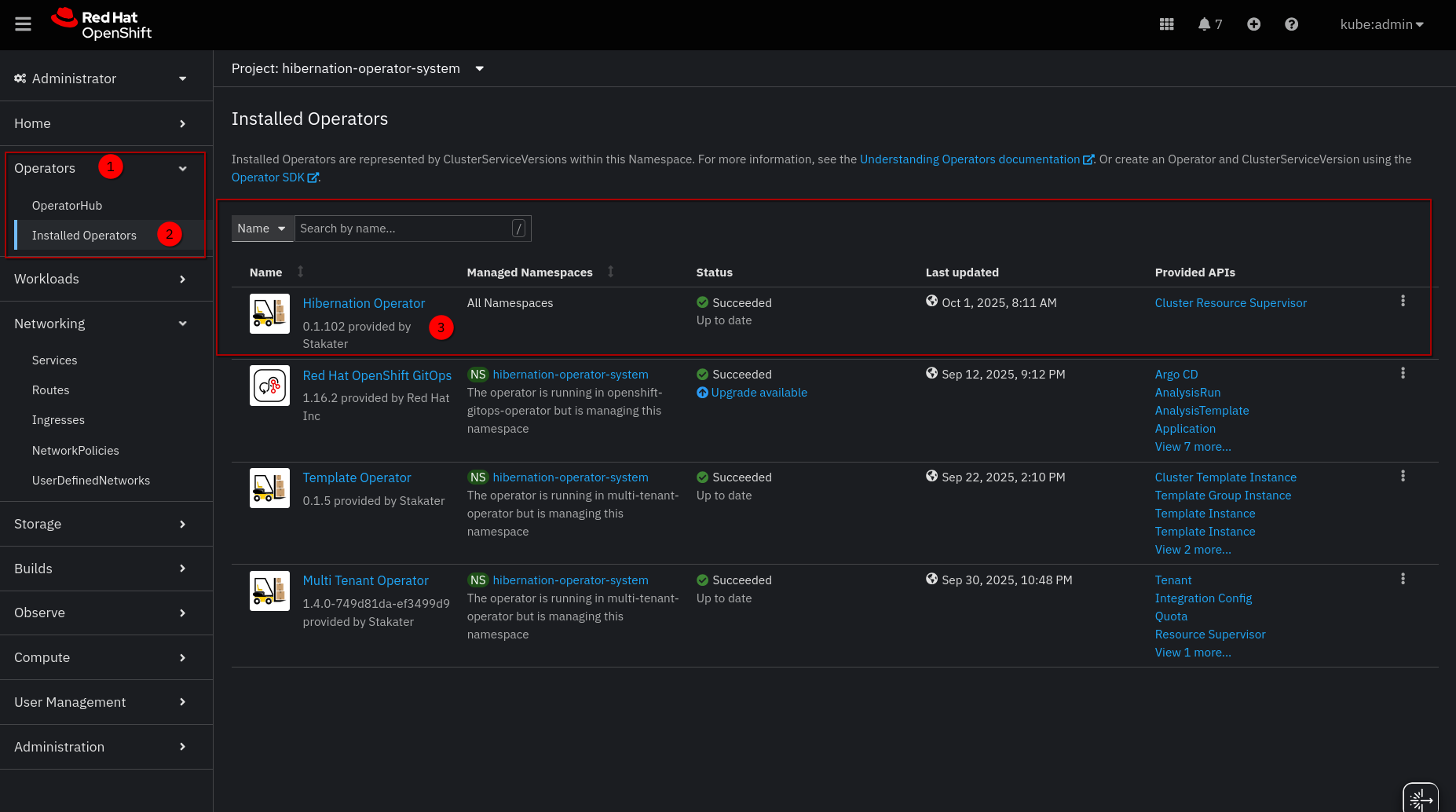
In the OpenShift Console:
- Go to Operators → Installed Operators
- Select the
hibernation-systemproject - Confirm the Hibernation Operator status is Succeeded
Or via CLI:
oc get csv -n hibernation-operator-system
oc get pods -n hibernation-operator-system
Wait until the hibernation-controller pod is Running.
Uninstall via OperatorHub UI#
⚠️ Warning: Uninstalling the operator does not delete your CRs (
ClusterResourceSupervisor,ResourceSupervisor). Workloads may remain asleep if not cleaned up.
Step 1: (Optional) Clean Up Hibernation Policies#
Delete any active hibernation resources to restore workloads:
# Delete all cluster-wide hibernation rules
oc delete clusterresourcesupervisors.hibernation.stakater.com --all
# Delete all namespace-scoped hibernation rules
oc delete resourcesupervisors.hibernation.stakater.com --all --all-namespaces
Step 2: Uninstall the Operator#
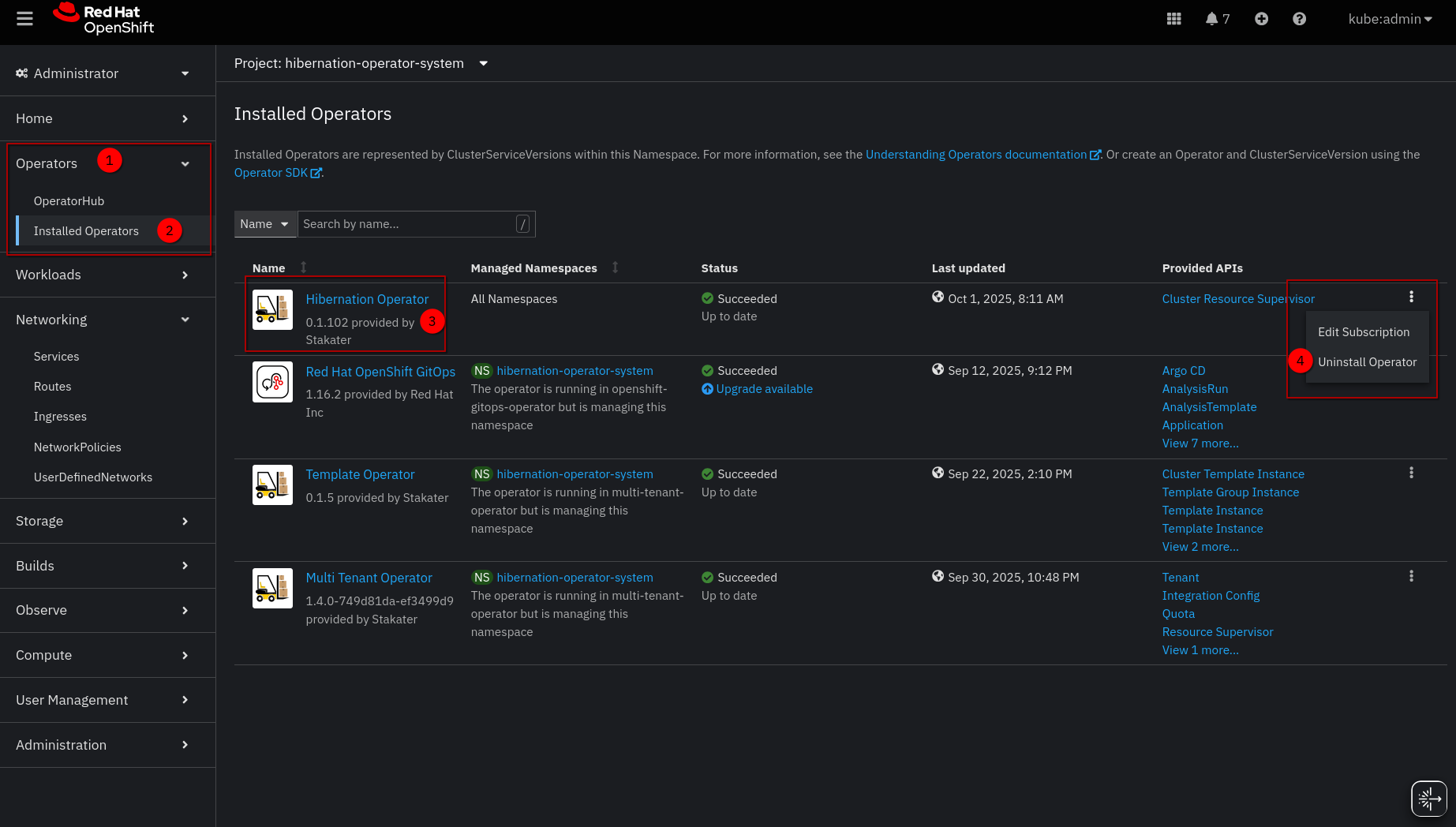
- In OpenShift Console, go to Operators → Installed Operators
- Find Hibernation Operator in the
hibernation-operator-systemproject - Click the three-dot menu → Uninstall Operator
- Confirm removal
Step 3: (Optional) Clean Up Leftover Resources#
To fully remove all traces:
# Remove namespace (includes RBAC, deployments, etc.)
oc delete namespace hibernation-operator-system
# Remove CRDs (only if no other instances exist)
oc delete crd clusterresourcesupervisors.hibernation.stakater.com
oc delete crd resourcesupervisors.hibernation.stakater.com
🔒 Note: CRD deletion is irreversible. Ensure no other tools depend on them.
Notes#
- The Hibernation Operator does not include a web console—it is a lightweight, API-driven operator.
- It integrates natively with OpenShift workloads (
Deployments,StatefulSets) and ArgoCD (if installed). - For production, use Manual approval and test upgrades in a staging cluster first.
- Full CRD documentation: