Workflow guide for Tronador#
Warning
The guide below is written as a SAAP customer's point of view. If you use Tronador independently, the guide below might not be applicable to you. However, you can still use this guide to get an idea of how the process works.
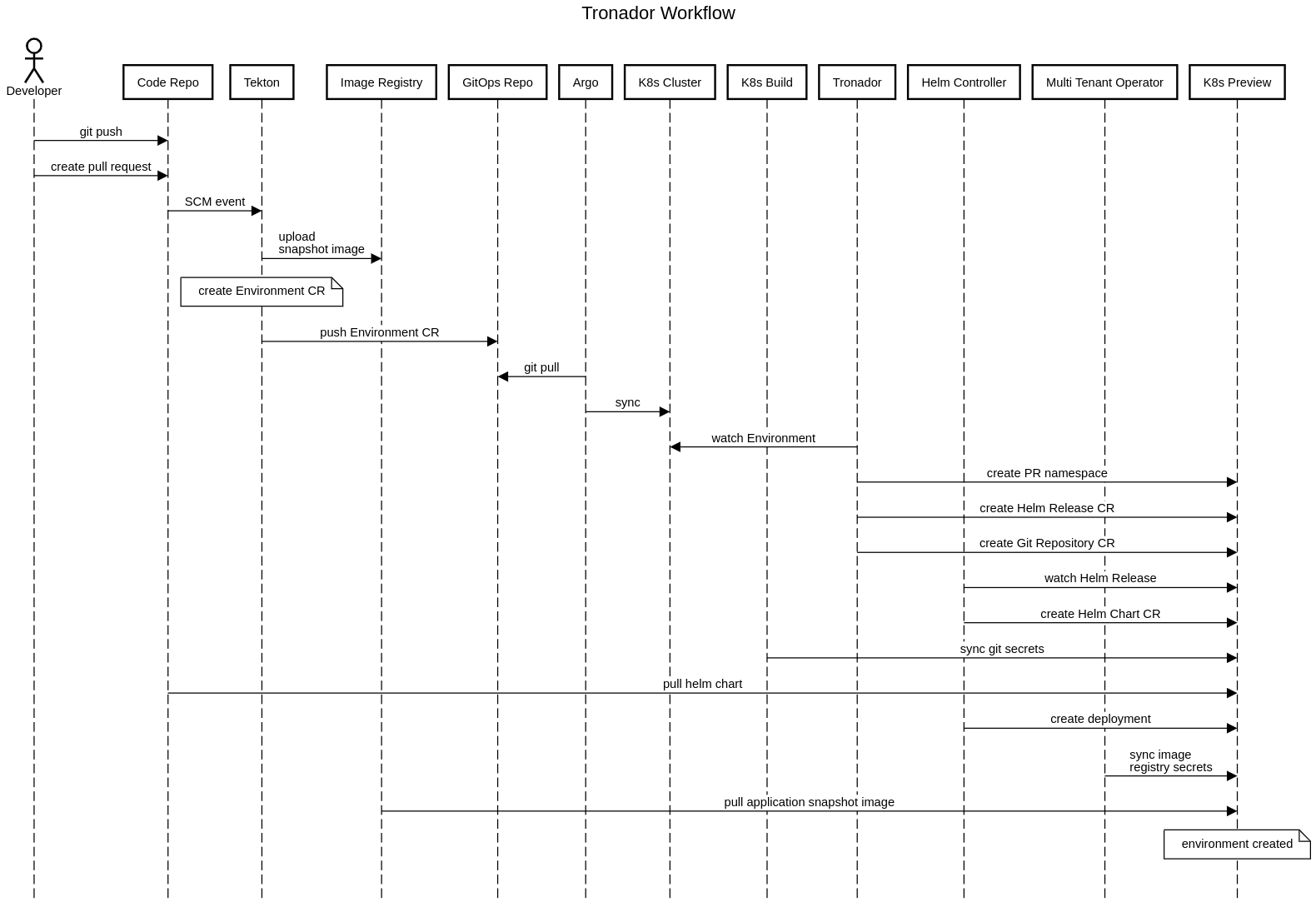
For Tronador to work, you need to add support for it in your Git Repository by adding a Tronador config file. Afterwards, a Tekton pipeline needs to be setup with the Tronador cluster task, and a cluster task that pushes the output EP to your GitOps repository. Test environments should then be created automatically every time a PR is created or updated. The entire Dynamic Test Environment (DTE) creation process is described below.
Tronador config file#
The Tronador config file is placed in the GitHub repository and is used to configure the Environment CR. Environment Provisioning will only work if the config file exists.
application:
chart_path: deploy
namespaceLabels:
kind: pr
team: gabbar
stakater.com/tenant: veeru
value_overrides:
application:
deployment:
image:
repository: { { APPLICATION_IMAGE_NAME } }
tag: { { APPLICATION_IMAGE_TAG } }
GitHub Event#
GitHub (or any other repository management system) events are used to trigger the Tronador pipeline. The pipeline is triggered whenever a PR is opened for a repository that supports Tronador.
Tekton Pipeline#
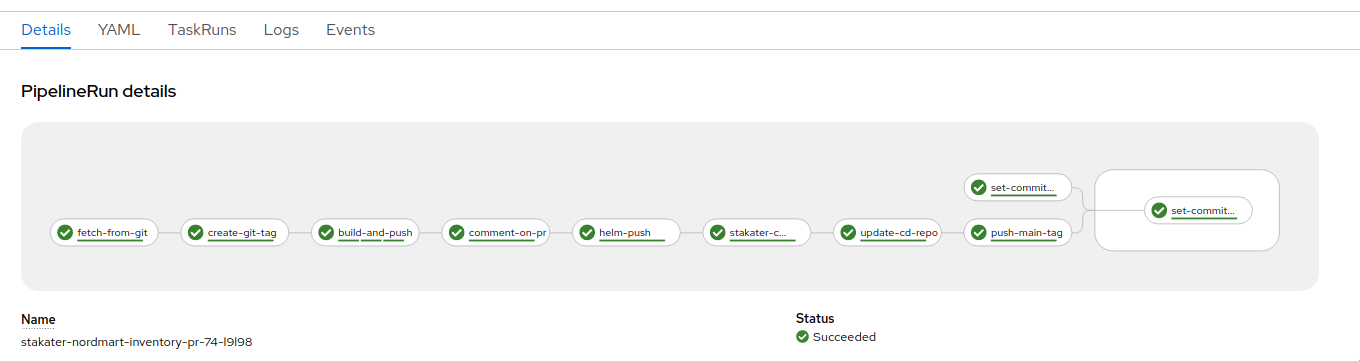
The Tekton Pipeline needs to watch the repo where Tronador is configured, so when a PR is created or updated it will trigger the Tekton pipeline to run. The pipeline will first create a docker image from the changes in your PR. It will then create an Environment CR by using the details in the config file, and replacing its APPLICATION_IMAGE_NAME and APPLICATION_IMAGE_TAG variables in the config file with the details about the created docker image. Finally, it will push the Environment to your GitOps repository.
GitOps Repository#
A successful pipeline run will create a new Environment CR, and push it to your GitOps repository.
ArgoCD push#
ArgoCD is a tool that can be used to watch a repo and push the changes to your cluster. In this case, it will push the Environment CR from your GitOps repository to your cluster.
Environment#
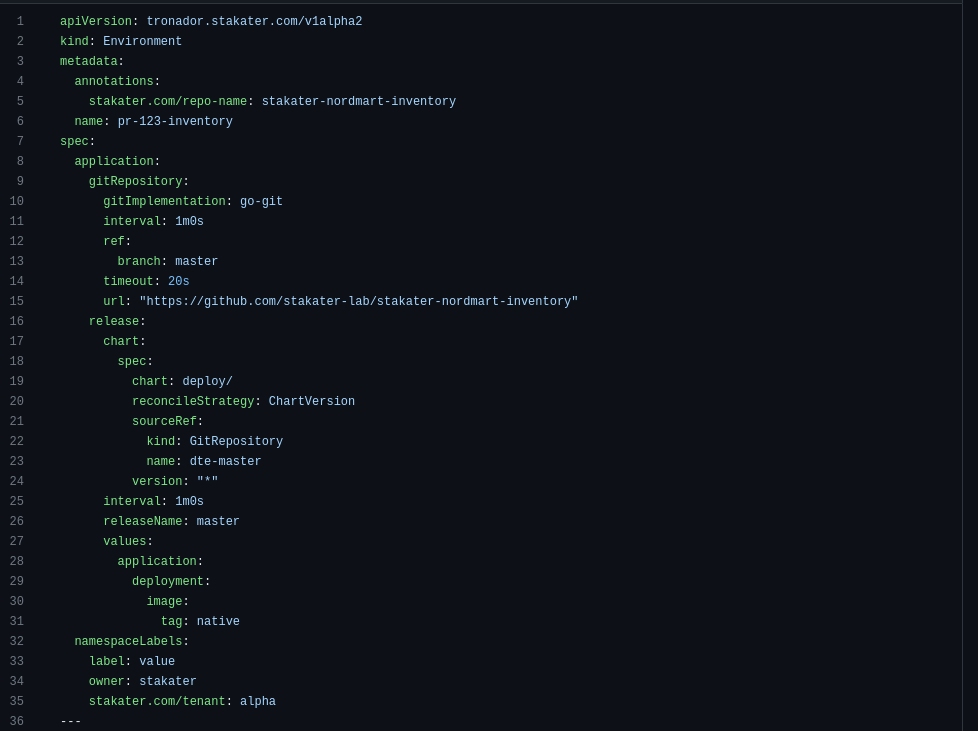
The Environment Custom Resource does the actual work of creating the test environment. It is responsible for creating the test environment, and for updating it when the image is updated. The process for this is to first create a namespace, then create HelmRelease and GitRepository resources within that namespace using details about the image to be deployed. These details are gotten from the pipeline and the Tronador config file.
apiVersion: tronador.stakater.com/v1alpha2
kind: Environment
metadata:
annotations:
stakater.com/repo-name: stakater-nordmart-inventory
name: pr-123-inventory
spec:
application:
gitRepository:
gitImplementation: go-git
interval: 1m0s
ref:
branch: master
timeout: 20s
url: "https://github.com/stakater-lab/stakater-nordmart-inventory"
release:
chart:
spec:
chart: deploy/
reconcileStrategy: ChartVersion
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: dte-master
version: "*"
interval: 1m0s
releaseName: master
values:
application:
deployment:
image:
tag: native
namespaceLabels:
label: value
owner: stakater
stakater.com/tenant: alpha
Helm Release#
Helm Releases are watched by the Helm Controller, which manages the creation of all resources listed in a referenced Helm chart. This chart is usually placed within the repo itself, and in this case Tronador passes along the reference to this chart from the Environment to the Helm Release. The only thing that is changed is the image to be deployed, which is passed along from the pipeline with each update to the PR and updated within the Helm release automatically.
apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2beta1
kind: HelmRelease
metadata:
name: dte-master
namespace: pr-123-inventory
spec:
chart:
spec:
chart: deploy/
reconcileStrategy: ChartVersion
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: dte-master
version: "*"
install:
remediation:
retries: 60
interval: 1m0s
releaseName: dte-master
values:
application:
deployment:
image:
tag: native
Git Repository#
A GitRepository resource is also created in addition to the HelmRelease. This resource specifically has details about where the Git Repository is, and what branch is being used.
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta2
kind: GitRepository
metadata:
name: dte-master
namespace: pr-123-inventory
spec:
gitImplementation: go-git
interval: 1m0s
ref:
branch: master
timeout: 20s
url: "https://github.com/stakater-lab/stakater-nordmart-inventory"
Secrets management#
Secrets for the Helm chart to be deployed are currently passed along from the Tronador config file, to the Helm release. Secrets for Helm chart and other required resources like image pull secret can be brought into Environment owned namespaces using Tronador Config CR.
You can also use Multi Tenant Operator's TemplateGroupInstance to pass secrets to the namespace that will be provisioned by the Environment by setting the proper label in your Tronador config file. An example for this workflow is provided here.
Application snapshot deployed#
After the entire above process is completed, the Helm Release will create a deployment that will deploy the pods for the application and its changes mentioned in the PR to the namespace created by the Environment.