HashiCorp Vault#
HashiCorp Vault is a tool for securely managing secrets. A secret is anything that you want to tightly control access to, such as API keys, passwords, or certificates. Vault provides a unified interface to any secret, while providing tight access control and recording a detailed audit log.
When you create a secret in Kubernetes it is stored in etcd as plain text, and the secret is also accessible to anyone that has access to your cluster. Vault solves this issue by providing a central secret management store that provides an additional layer of security using its authentication methods. Secrets are only accessible when you provide a corresponding authentication token.
There are two kinds of secrets stored in Vault for SAAP:
- Secrets for managed applications provided by Stakater, such as Nexus repository credential:
- Users only have read permissions
- The Vault path is
managed-addons/*
- Tenant specific secrets:
- A
KVv2 secret engine is enabled on theTENANT_NAME/kvpath by default - Users can enable/disable secret engines on
TENANT_NAME/*paths and create/delete/update/read secrets through them
- A
Users can manage secrets via Vault UI or Vault CLI.
Manage Vault secrets via UI#
Users included in any tenants can access the Vault UI using OIDC authentication.
Once logged in, users can do all actions on the path TENANT_NAME/*:
- Enable/disable any kinds of secret engines
- Create/update/get/list/delete secrets
Authentication#
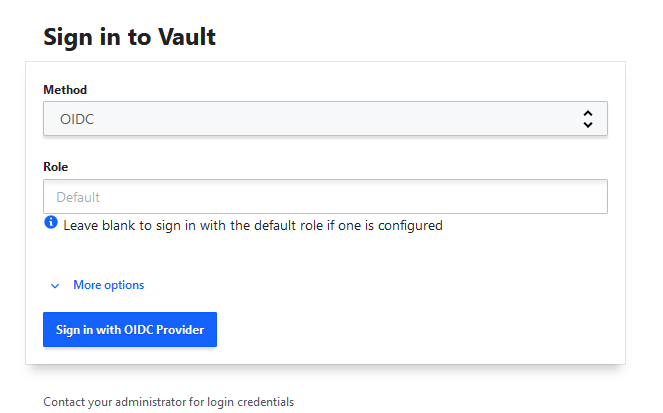
To log in to Vault via the UI:
- Access Vault via Forecastle or
https://stakater-vault-openshift-stakater-vault.CLUSTER_DOMAIN - Select the
OIDCmethod - Keep
RoleasDefault -
Click
Sign in with OIDC Provider: -
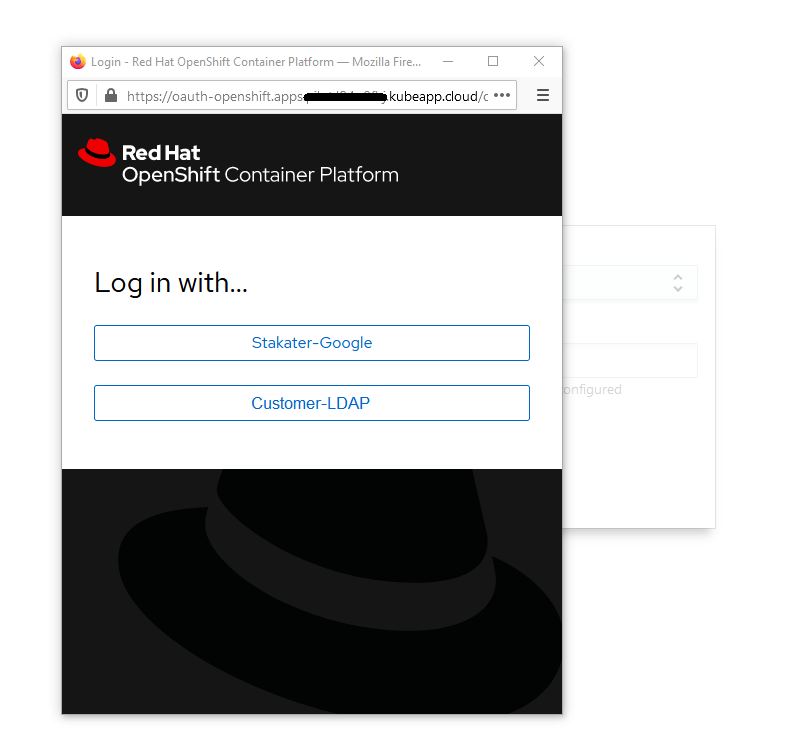
A login dialogue will pop up. The browser needs to allow popup dialogues:
Enable secret engines#
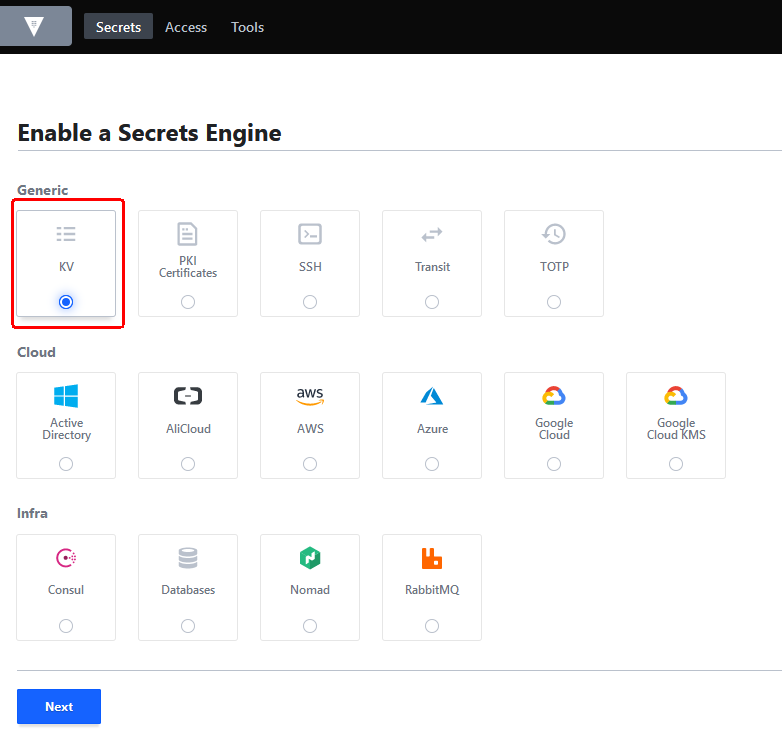
To enable a secrets engine:
-
Click on the Secrets tab
-
Under Secrets Engines, select
Enable new engine: -
Select an engine and click next:
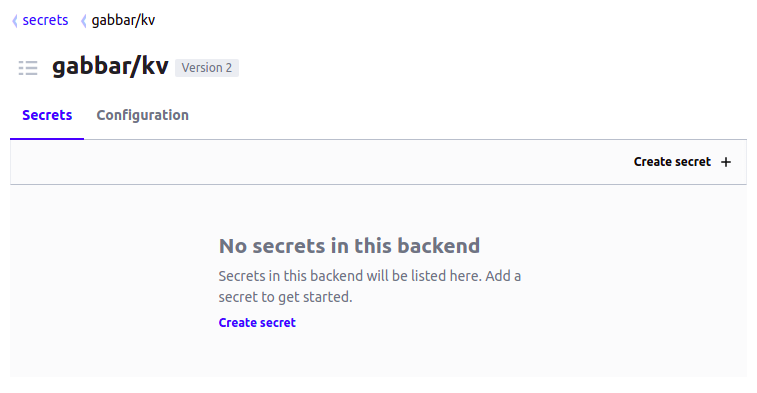
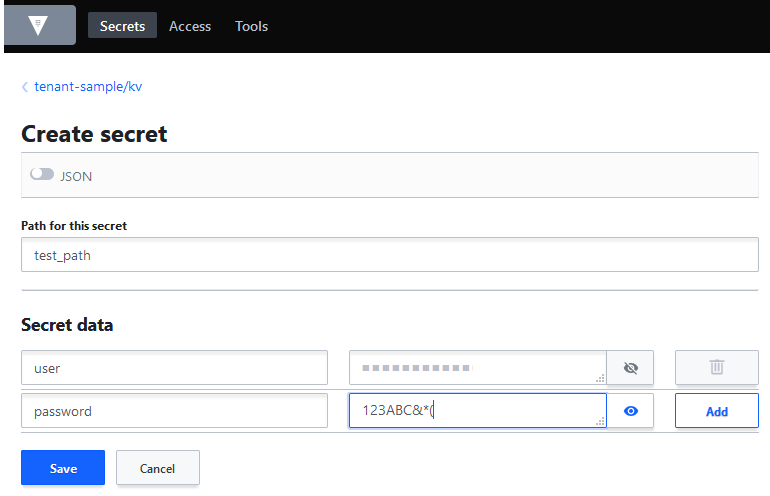
Create secrets#
To create a secret:
- Click on your
TENANT/kvpath -
Click on the
Create Secretbutton: -
Provide key-value pair to add secret:
Manage Vault secrets via CLI#
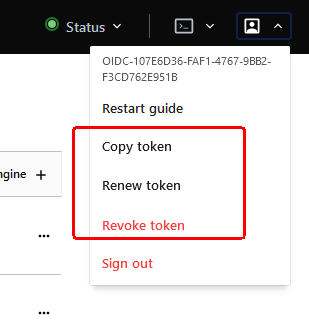
To use the Vault CLI, a token is required. Users can get/renew/revoke a token from the UI:
-
Click on the user account:
-
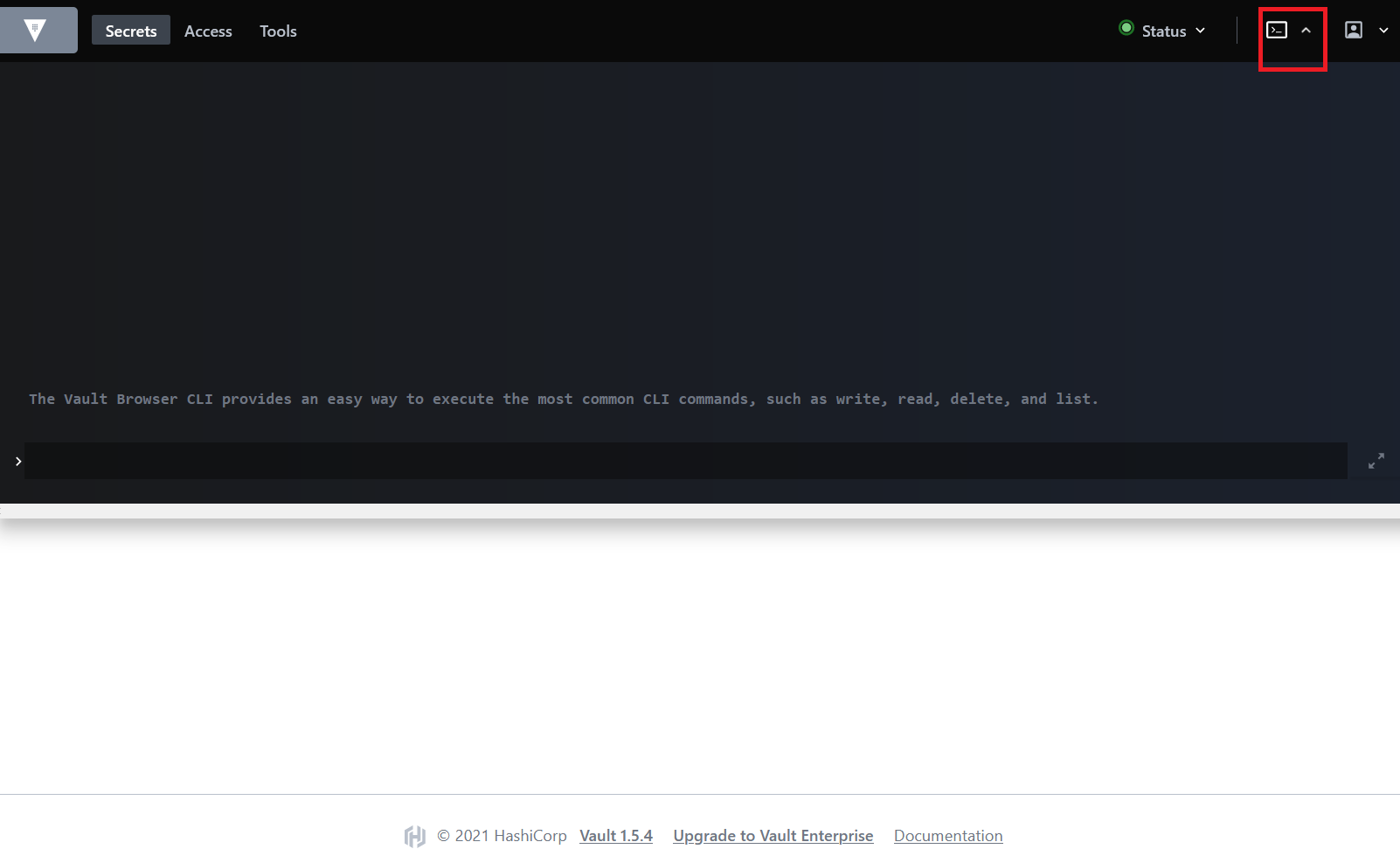
Once a token is fetched, users can use the terminal provided by the UI, so there is no need to install the Vault CLI:
-
If using the Vault CLI, login with the token:
vault login token=${TOKEN}
Consume Vault secrets#
SAAP supports 3 different ways to consume secrets from Vault:
- Option 1 (Recommended): Consume Vault secret via ExternalSecret
- Option 2: Consume Vault secret via a Volume
- Option 3: Consume Vault secret via Environment Variable
Below you can find step-by-step guides to consume secrets via the different options.
Option 1: Consume Vault secret via ExternalSecret#
Kubernetes secret by default do not support storing or retrieving secret data from external secret management systems such as Vault. External Secrets solves this problem by providing access to secrets stored externally. It does this by adding an ExternalSecret object to Kubernetes using a CustomResourceDefinition.
SAAP comes with fully managed External Secrets Operator to integrate with Vault and makes it extremely easy to consume secrets from Vault:
-
Add
tenant-vault-accesstemplate to the tenant:apiVersion: tenantoperator.stakater.com/v1alpha1 kind: Tenant metadata: name: gabbar spec: users: owner: - user1 - user2 quota: medium namespacetemplate: templateInstances: - spec: template: tenant-vault-access sync: true -
Enable
externalSecretin yourdeploy/values.yamland provide details of the secret path in Vault:externalSecret: enabled: true secretStore: name: tenant-vault-secret-store files: inventory-postgres: #Name of Kubernetes Secret data: postgresql-password: #Name of Kubernetes Secret Key remoteRef: key: inventory-postgres #Name of Vault Secret property: postgresql-password #Name of Vault Secret Key
When a secret is updated in Vault, the pod is automatically restarted by Reloader.
Option 2: Consume Vault secret via a Volume#
To mount Vault secret in a volume do the following:
-
Add label in
serviceAccountso it can be granted Vault read access to secret path:serviceAccount: enabled: true additionalLabels: stakater.com/vault-access: "true" -
Enable
SecretProviderClassobject in Helm values and define key and value path of Vault:secretProviderClass: enabled: true name: postgres-secret roleName: '{{.Release.Namespace}}' objects: - objectName: postgresql-password secretPath: gabbar/data/postgres secretKey: postgresql-password -
Define volume in Helm values that use above created
SecretProviderClass:deployment: volumes: - name: postgres-secret csi: driver: secrets-store.csi.k8s.io readOnly: true volumeAttributes: secretProviderClass: postgres-secret -
Mount this volume in the container:
volumeMounts: - name: postgres-secret readOnly: true mountPath: /data/db-creds
Option 3: Consume Vault secret via Environment Variable#
To mount Vault secret in an environment variable:
-
Enable
SecretProviderClassobject in Helm values and define key/value path and secret objects in Vault:secretProviderClass: enabled: true name: postgres-secret roleName: '{{.Release.Namespace}}' objects: - objectName: postgresql-password secretPath: gabbar/data/postgres secretKey: postgresql-password secretObjects: - data: - key: postgres-password objectName: postgresql-password secretName: postgres-secret type: Opaque
The value of secretName will be the name of the Kubernetes secret.
-
Define volume in Helm values that use above created
SecretProviderClass:deployment: volumes: - name: postgres-secret csi: driver: secrets-store.csi.k8s.io readOnly: true volumeAttributes: secretProviderClass: postgres-secret -
Mount this volume in the container:
volumeMounts: - name: postgres-secret readOnly: true mountPath: /data/db-credsVolume mount is required in order to create a Kubernetes secret.
-
This secret can be used as an environment variable:
env: - name: POSTGRES_PASSWORD valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: postgres-secret key: postgres-password
Here is a working example.
Your secret should be available at the path defined above in Vault; a change in secret value in Vault will automatically restart the application by Stakater Reloader.