Configure Repository Secret for ArgoCD#
GitHub#
Configure token or SSH keys#
Use the following links:
- For token access
- PAT (Classic):
Create a personal access tokenwith the required "repo permissions" for GitOps repositories. Note: This PAT can be used for all repos, so to segregate your usual repositories from GitOps, you can use "Fine-grained tokens" in GitHub. -
PAT (Fine-grained): Allows you to select repositories from your GitHub organization which can use the token.
Create a fine-grained tokenwith the below-mentioned permissions for your GitOps repos:- Actions (Read and write)
- Administration (Read and write)
- Commit statuses (Read only)
- Contents (Read and write)
- Deployments (Read only)
- Metadata (Read only) _
- Pull requests (Read and write)
- PAT (Classic):
Once we create a PAT, it cannot be edited. Using same PAT (fine-grained) for multiple repositories, requires the repos to be created first and then added in the PAT.
By properly configuring the permissions and access levels for the PAT, you can ensure that it is only used for authorized actions within both the Infrastructure GitOps and Application GitOps workflows while maintaining the required level of security and separation of concerns.
- For SSH Access
Generate SSH Key PairAdd SSH Public key to your GitHub AccountorAdd Deploy Key to your RepositoryNote: A deploy key is specific to a single repository and cannot be used for multiple repositories whereas, a single SSH key can be used for multiple repositories.
Kubernetes#
Create a Kubernetes Secret with Token or SSH key#
Create a Kubernetes Secret in ArgoCD namespace with repository credentials. Each repository secret must have a URL field and, depending on whether you connect using https, SSH, username and password (for https), sshPrivateKey (for SSH).
Example for https:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: private-repo
namespace: argocd-ns
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: repository
stringData:
type: git
url: https://github.com/argoproj/private-repo
# Use a personal access token in place of a password.
password: my-pat-or-fgt
username: my-username
Example for SSH:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: private-repo
namespace: argocd
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: repository
stringData:
type: git
url: git@github.com:argoproj/my-private-repository
sshPrivateKey: |
-----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
...
-----END OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
More Info on Connecting ArgoCD to Private Repositories here
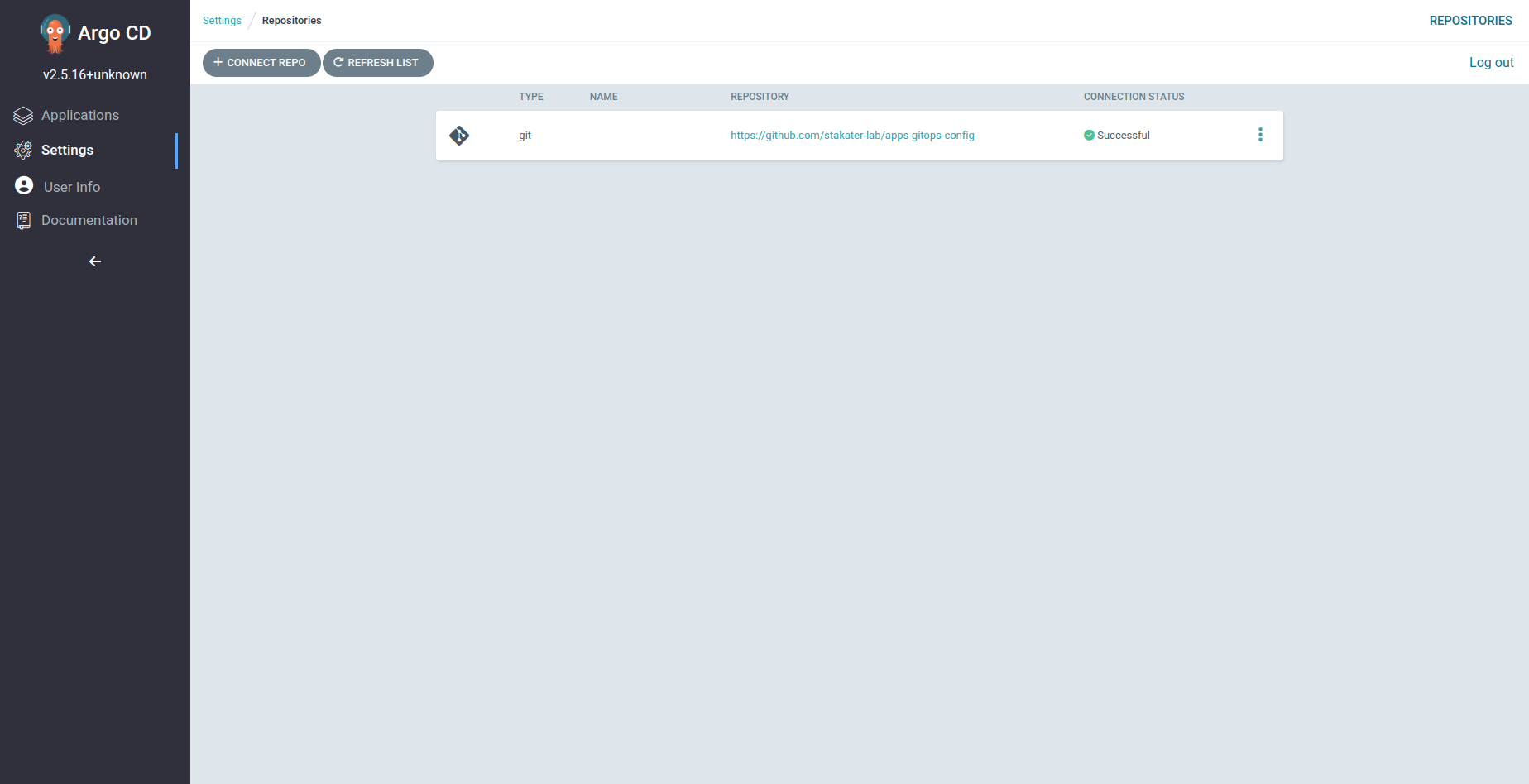
Login to the ArgoCD UI. Click Setting from left sidebar, then Repositories to view connected repositories.
Make sure connection status is successful
Create an External Secret#
Ask
stakater-adminor user belonging tocustomer-root-tentto add this secret via Vault and External Secrets to ArgoCD namespace.
Possible Issues#
If connection status is failed, hover over the ❌ adjacent to Failed to view the error.
SSH Handshake Failed: Key mismatch#
Related GitHub Issue: here
If you see the following error. Check argocd-ssh-known-hosts-cm config map in ArgoCD namespace to verify that public key for repository server is added as ssh_known_hosts.
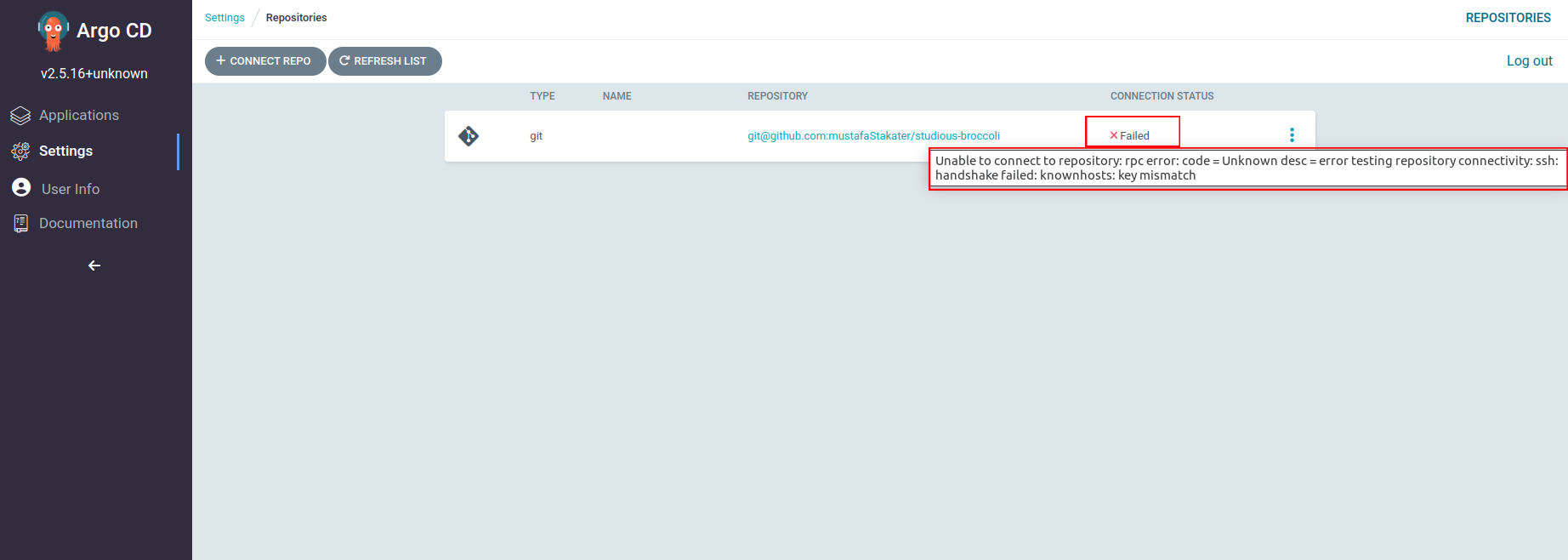
Some known hosts public keys might be missing in argocd-ssh-known-hosts-cm for older ArgoCD versions, Find full list of public keys against repository server here.
Note
If the error persists, contact Stakater Support to review it.