Access Postgres CLI via Port Forward#
This documentation will help to connect to managed Postgres via psql using port forward.
CLI Setup#
The first step is to setup psql on your local machine. For this, go through following steps. If you already have CLI setup, you can skip this section.
-
Run following command in terminal:
-
Run following command to verify CLI installation:
Create Port Forwarding to Postgres Service#
Before running psql command we need to port forward to Postgres Pod running in cluster. To achieve this, perform following steps:
-
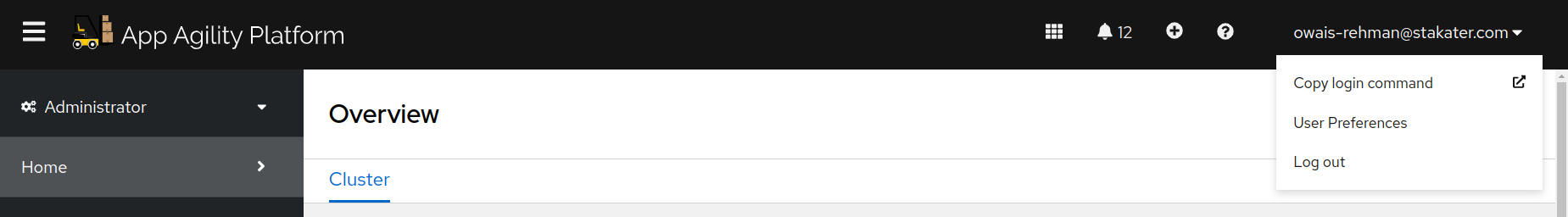
In OpenShift console, click on your username on top right corner and click
Copy login commandas shown below: -
Click on
Display Tokenand then copyoc logincommand. - Run this command inside your terminal. Now you have access to interact with your cluster using terminal.
-
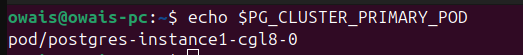
Run following command to locate the pod to which we need to create port forward.
PG_CLUSTER_PRIMARY_POD=$(oc get pod -n <postgres-namespace> -o name -l postgres-operator.crunchydata.com/cluster=<postgres-cluster>,postgres-operator.crunchydata.com/role=master)Here
<Postgres-namespace>is the name of namespace where Postgres is deployed (In current case its value iscrunchy-postgres-instance). This name might be different for you. You can ask about this to cluster admin.<Postgres-cluster>is the name of cluster in Postgres that usually get created at time of deployment (In current case its value ispostgres). You can ask about its name from cluster admin as well. -
Upon printing the value stored in variable mentioned above, you'll get an output similar to one shown below:
-
Run the following command to create port forward.
-
At this moment, you need to open a second terminal (while keeping this running) and run following command:
$PGUSERis a reference to a variable that must be set (or you can replace this with username) used to connect to Postgres. This can easily be retrieved from Vault.-
$PGDATABASEcontains name of the database that you want to connect to. This can also be retrieved from Vault. -
This should result in following output:
-
Paste in the password that you can get from Vault.
-
At this moment, you should have access to
psql. You can run\qat anytime to exit out of this terminal access.
Caveat#
When using oc port-forward, the connection can be fragile. This has been reported as an issue. A workaround is to disable SSL mode.